Vitamin D is an essential fat-soluble vitamin which helps the body absorb calcium and phosphorus, making it crucial for bone health. It also plays an important role in supporting immune health. "Vitamin D is a hormone that affects calcium absorption, and also has recognized effects on the immune system," says Dr. Donald Ford, MD, a family medicine physician at Cleveland Clinic. Here are five things that happen when you take vitamin D every day.
Vitamin D and COVID-19
While taking vitamin D cannot prevent COVID-19, studies show it can help prevent disease severity—one study showed that people with vitamin D deficiency were 14 times more likely to have a critical case of COVID. "Results suggest that it is advisable to maintain normal levels of vitamin D," says Dr. Amiel Dror from the Galilee Medical Center and Azrieli Faculty of Medicine. "This will be beneficial to those who contract the virus. There is a clear consensus for vitamin D supplementation on a regular basis as advised by local health authorities as well as global health organizations."
Vitamin D and Bone Health

Vitamin D is essential for bone and muscle health in both children and adults, but doctors warn taking too much can have the opposite effect. "People often assume that if some is good, more is better," says Dr. JoAnn E. Manson, the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women's Health at Harvard Medical School. "This is generally not the case, and certainly is not true of vitamin D. While there is no question that vitamin D and calcium are essential to bone health, it appears that very high doses of vitamin D don't provide further benefits for bone health and may actually have a harmful effect." So how much is ideal? 600 IU is the recommended daily amount of vitamin D, according to the NIH.
Foods High In Vitamin D
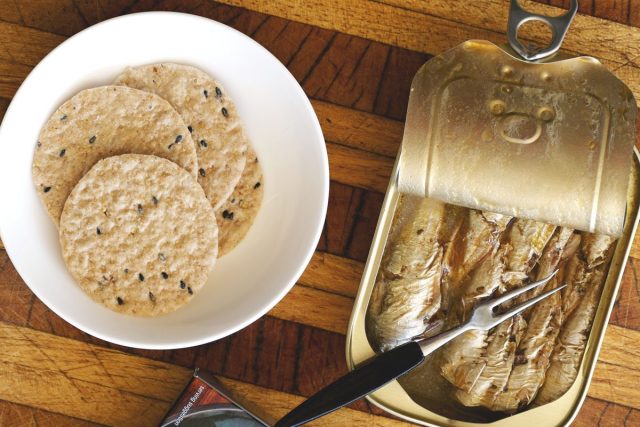

"Many common foods are fortified with vitamin D (milk, juices, cereal) and foods that are natural sources of vitamin D include oily fish such as salmon and sardines, and some cheeses and mushrooms," says Dr. Ford. What about getting vitamin D from sun exposure? "This has to be balanced with concerns about skin cancer risk," says Dr. Ford. "A rule of thumb for sun exposure is that 15 minutes daily exposure on the hands and face is sufficient."
Vitamin D and Gut Bacteria
Vitamin D can encourage microbiome diversity, researchers say. "We were surprised to find that microbiome diversity—the variety of bacteria types in a person's gut—was closely associated with active vitamin D, but not the precursor form," says Deborah Kado, MD, director of the Osteoporosis Clinic at UC San Diego Health. "Greater gut microbiome diversity is thought to be associated with better health in general."
Vitamin D and Brain Function

Vitamin D plays an important role in brain health. "Vitamin D is neuroprotective, regulates the immune system and helps with calcium balance," says Thomas Burne, PhD. "It is also involved with regulating many genes important for brain function. Although vitamin D is thought of as a vitamin, it acts as a neurosteroid and plays important roles in the brain."