HSBC allowed fraudsters to transfer millions of dollars around the world even after it had learned of their scam, leaked secret files show.
Britain's biggest bank moved the money through its US business to HSBC accounts in Hong Kong in 2013 and 2014.
Its role in the $80m (£62m) fraud is detailed in a leak of documents - banks' "suspicious activity reports" - that have been called the FinCEN Files.
HSBC says it has always met its legal duties on reporting such activity.
The files show the investment scam started soon after the bank was fined $1.9bn (£1.4bn) in the US over money laundering. It had promised to clamp down on these sorts of practices.
The scam is known as a Ponzi scheme - a notorious type of investment racket that pays existing stakeholders with money collected from new members.
Lawyers for duped investors say the bank should have acted sooner to close the fraudsters' accounts.
The documents leak includes a series of other revelations - such as the suggestion one of the biggest banks in the US may have helped a notorious mobster to move more than $1bn.
What are the FinCEN Files?
The FinCEN Files are a leak of 2,657 documents, at the heart of which are 2,100 suspicious activity reports, or SARs.
SARs are not evidence of wrongdoing - banks send them to the authorities if they suspect customers could be up to no good.
By law, they have to know who their clients are - it's not enough to file SARs and keep taking dirty money from clients while expecting enforcers to deal with the problem. If they have evidence of criminal activity, they should stop moving the cash.
The leak shows how money was laundered through some of the world's biggest banks and how criminals used anonymous British companies to hide their money.
The SARs were leaked to the Buzzfeed website and shared with the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ). Panorama led the research for the BBC as part of a global probe. The ICIJ led the reporting of the Panama Papers and Paradise Papers leaks - secret files detailing the offshore activities of the wealthy and the famous.
Fergus Shiel, from the consortium, said the FinCEN Files are an "insight into what banks know about the vast flows of dirty money across the globe… [The] system that is meant to regulate the flows of tainted money is broken".
The leaked SARs had been submitted to the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network, or FinCEN between 2000 and 2017 and cover transactions worth about $2 trillion.
FinCEN said the leak could impact US national security, risk investigations, and threaten the safety of those who file the reports.
But last week it announced proposals to overhaul its anti-money laundering programmes.
The UK also unveiled plans to reform its register of company information to clamp down on fraud and money laundering.
What was the Ponzi scam?
 FACEBOOK
FACEBOOKThe investment scam that HSBC was warned about was called WCM777. It was started by Chinese national Ming Xu. Little is known about how he came to be living in the US, although he claims to have studied for an MA in California.
Basing himself in the Los Angeles area, Xu - or "Dr Phil" as he styled himself - acted as a pastor at evangelical churches.
Xu said he was operating a global investment bank, World Capital Market, that would pay out 100% profit in a 100 days. In reality, he was running the WCM777 Ponzi scheme.
Through travelling seminars, Facebook and webinars on YouTube, it raised $80m selling supposed investment opportunities in cloud computing.
Thousands of people from the Asian and Latino communities were taken in. The fraudsters used Christian imagery and targeted poor communities in the US, Colombia and Peru. There were also victims in other countries, including the UK.
But the impact were not just financial. The scheme led to the death of investor Reynaldo Pacheco, who was found under water on a wine estate in Napa, California, in April 2014. Police say he had been bludgeoned with rocks.

He signed up to the scheme and was expected to recruit other investors. The promise was everyone would get rich.
A woman Mr Pacheco, 44, introduced lost about $3,000. That led to the killing by men hired to kidnap him.
"He literally was trying to… make people's lives better, and he himself was scammed, and conned, and he unfortunately paid for it with his life," said Sgt Chris Pacheco (no relation), one of the officers who investigated the killing.
Reynaldo, he said, "was murdered for being a victim in a Ponzi scheme".
By then, regulators in California had already told HSBC it was investigating WCM777 - and alerted its residents to the fraud. This happened in September 2013
And California, along with Colorado and Massachusetts, took action against WCM for selling unregistered investments.
HSBC did spot suspicious transactions going through its systems. But it was not until April 2014, after US financial regulator the Securities and Exchange Commission filed charges, that the WCM777 accounts at HSBC in Hong Kong were shut.
By that time there was nearly nothing left in them.
What do the suspicious activity reports show?
HSBC filed its first SAR about the scam on 29 October 2013 relating to more than $6m sent to the fraudsters' accounts in Hong Kong.


Bank officials said there was "no apparent economic, business, or lawful purpose" for the transactions - and noted allegations of "Ponzi scheme activities".
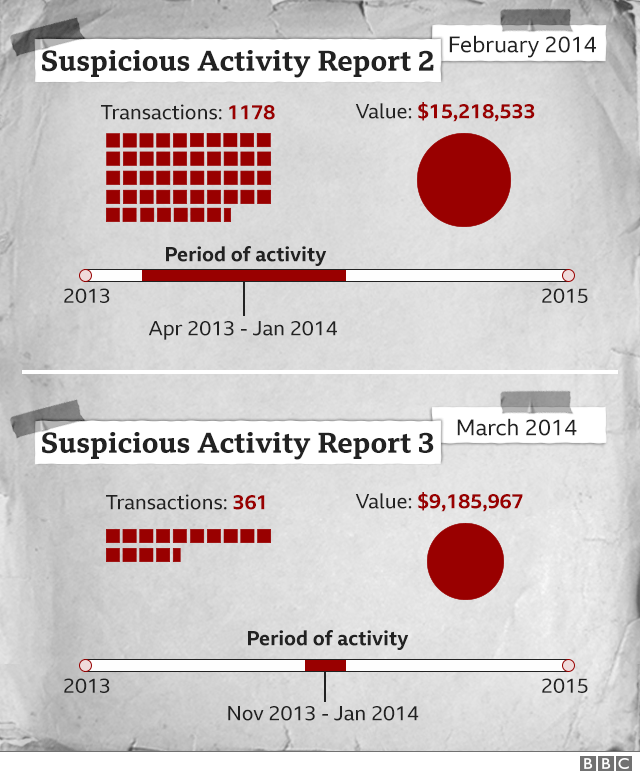
A second SAR in February 2014 identified $15.4m in suspicious transactions, and a "Potential Ponzi scheme".
A third report in March related to a company associated with WCM777 and nearly $9.2m, and noted the regulatory moves by US states and an investigation ordered by Colombia's president.

What did HSBC do?
The WCM777 scheme emerged months after HSBC avoided a US criminal prosecution over money laundering by Mexican drug barons. It did so by agreeing to improve procedures.
Analysis by the ICIJ shows that between 2011 and 2017 HSBC identified suspicious transactions moving through accounts in Hong Kong of more than $1.5bn - about $900m linked to overall criminal activity.
But the reports failed to include key facts about customers, including the ultimate beneficial owners of accounts and where the money came from.
Banks are not allowed to talk about suspicious activity reports.
HSBC said: "Starting in 2012, HSBC embarked on a multi-year journey to overhaul its ability to combat financial crime across more than 60 jurisdictions… HSBC is a much safer institution than it was in 2012."
The bank added the US authorities had determined that it "met all of its obligations under the [agreement struck with US prosecutors]".
Xu was eventually arrested by the Chinese authorities in 2017 and jailed for three years over the scam.
Speaking to the ICIJ from China, Xu said HSBC had not contacted him about his business. He denied WCM777 was a Ponzi scheme, saying it was wrongly targeted by the SEC and his aim had been to build a religious community in California on more than 400 acres of land.
What is a Ponzi scheme?
A Ponzi scheme - named after early 20th Century conman Charles Ponzi - does not generate profits from the cash it raises. Instead investors are paid a return from money coming in from other new investors.
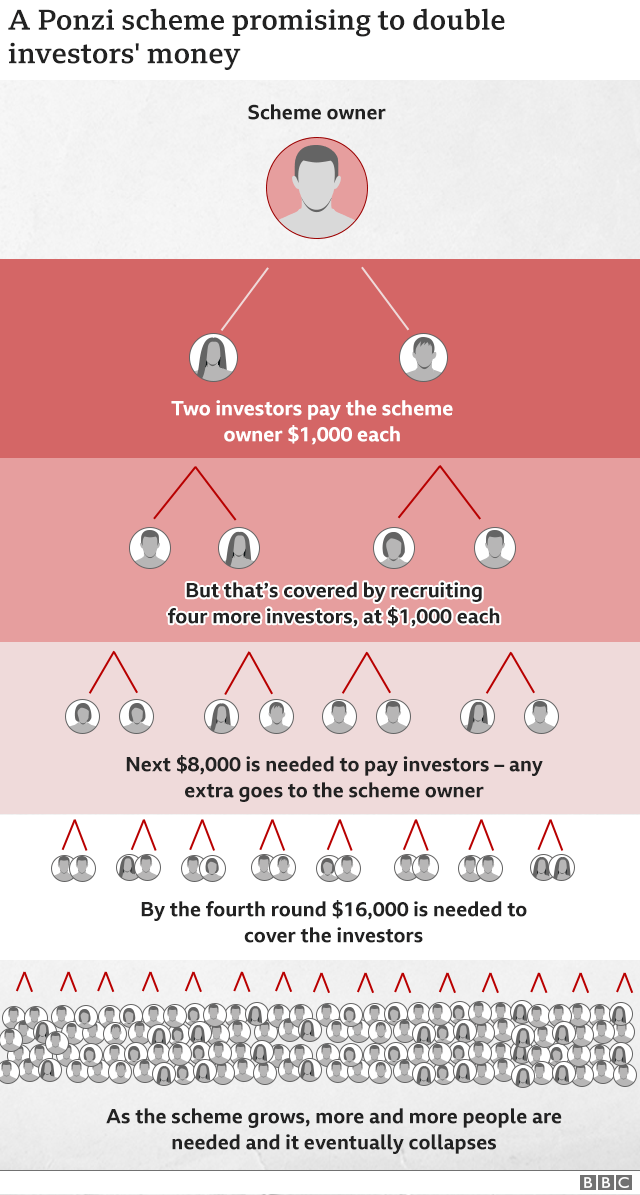

More and more investors are needed to cover these payments. Meanwhile, the owners of the scheme move money into their own accounts.
A Ponzi scheme will collapse if it cannot find enough new investors.
What else did the leak find?
The FinCEN Files also show how multinational bank JP Morgan may have helped a man known as the Russian mafia's boss of bosses to move more than a $1bn through the financial system.
Semion Mogilevich has been accused of crimes including gun running, drug trafficking and murder.
 FBI
FBIHe should not be allowed to use the financial system, but a SAR filed by JP Morgan in 2015 after the account was closed, reveals how the bank's London office may have moved some of the cash.
It details how JP Morgan, provided banking services to a secretive offshore company called ABSI Enterprises between 2002 and 2013, even though the firm's ownership was not clear from the bank's records.
Over one five-year period, JP Morgan sent and received wire transfers totalling $1.02bn, the bank said.

The SAR noted ABSI's parent company "might be associated with Semion Mogilevich - an individual who was on the FBI's top 10 most wanted list".
In a statement, JP Morgan said: "We follow all laws and regulations in support of the government's work to combat financial crimes. We devote thousands of people and hundreds of millions of dollars to this important work."

The FinCEN Files is a leak of secret documents which reveal how major banks have allowed criminals to move dirty money around the world. They also show how the UK is often the weak link in the financial system and how London is awash with Russian cash.
The files were obtained by BuzzFeed News which shared them with the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ) and 400 journalists around the world. Panorama has led research for the BBC.
No comments:
Post a Comment